University and Laboratory
Medical and science laboratory students who lack the clinical experience and expertise are at risk of sharps cuts from scalpel usage.
Scalpel injuries represent undue burden costs not only to the students but also to the university.
Although the risk of blood-borne infections from a single sharps injury is low, its consequences to an infected medical student can impact their long-term health as well as career-lasting impacts as it may restrict their career pathways.
Quick statistics on students injury risks*

Per 1000 Student-Hours of Dissection

Of Medical Students Have Had a Sharps and Needlestick Injury

Did Not Report the Injury
Scalpel Cuts Can Cause:
Blood-borne infection such as HBV, HCV, or HIV
Severed digital nerve and/or tendon
Psychological distress and/or trauma
Delayed graduation and loss of productivity
Career pathways derailment
Costs for an uncomplicated scalpel injury
US$ 550 – US$ 3000
Cost if the injury requires surgery and rehab
US$ 15000 – US$ 100000
In addition to the post-exposure management costs, there may be hidden costs such as student compensation, university or non-compliance penalties.
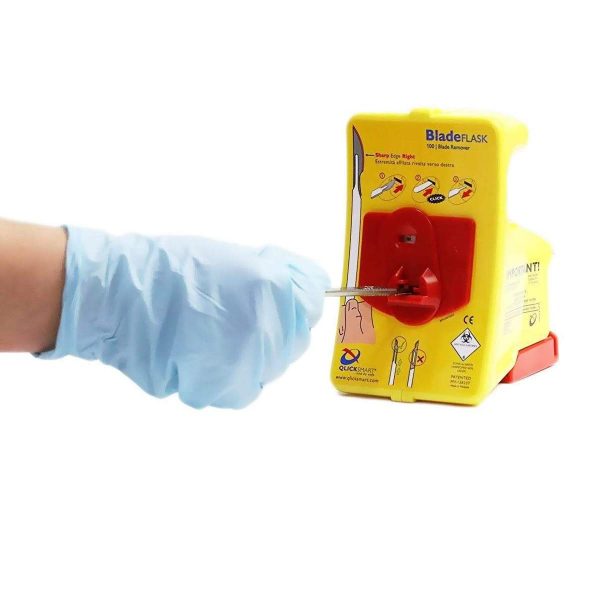
Preventing Cuts using the Qlicksmart BladeFLASK
- Removes up to 100 used scalpel blades
- Automatic safety mechanism removes and contains your scalpel blades using only one hand.
- Certified and medically approved sharps container.
- Can be attached to a wall or bench with the reusable Mounting Bracket.
- Dispose by placing it in your medical waste bin.
Qlicksmart BladeFLASKs are a quick and simple way to remove scalpel blades.

With the mounting bracket, the BladeFLASKs are placed in several stationary points within the laboratory, scalpel blade removal can be completed at point of use.

Automatic containment of used scalpel blades ensures that all students are protected from injury.

They work within your standard safety curriculum
- Fast implementation process
- Less training (compared to forceps)
- Compatible with wide range of blades

Qlicksmart devices have safely removed over 70 million contaminated scalpel blades, and prevented up to 150,000 injuries around the world.
Download here a PDF flyer version of this page.